Continuous Delivery Using Buildspecyml Aws Agular
In this article, I will show how to automate your deployment of the angular app to AWS S3 service by creating a pipeline on AWS Codepipeline service – in short, we will do CI/CD for an angular project. In Case, you are wondering what these AWS services are:
AWS Codepipeline
AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed continuous delivery service that helps you automate your release pipelines for fast and reliable applications.
Read more from the official docs, here.
AWS S3
Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is an object storage service that offers industry-leading scalability, data availability, security, and performance.
Read more from the official docs, here.
Since this article is more focused on automating deployment, I will not discuss these AWS services in detail. But, enough talk, let's see it broken up into steps, practically:
1) Create an Angular Project
Most of the time, you will probably have a project that you want to deploy, but if you just want to play with it, you have to create it by typing in the command prompt:
ng new angular-aws-app where angular-aws-app will be your app name.
Now, after successfully creating your project, go to github.com and create a repository for your app and push your code to your repo master branch.
2) Create Pipeline on AWS Code-Pipeline service
 After pushing your initial code on Github, we need to create a pipeline or automated process that will be responsible for deploying our code to Amazon S3 from Github repo. But, for this, you will need an AWS account so that you can access their services. You can create your account here for free tier, which will be free for 365 days. After creating your account, you will see a dashboard console.
After pushing your initial code on Github, we need to create a pipeline or automated process that will be responsible for deploying our code to Amazon S3 from Github repo. But, for this, you will need an AWS account so that you can access their services. You can create your account here for free tier, which will be free for 365 days. After creating your account, you will see a dashboard console.
 Type
Type code pipeline, click to that service, and go to pipelines in the sidebar to create a new pipeline for your app. You'll see an orange button on the top right corner to create a new pipeline.
 First, we set up our pipeline name to
First, we set up our pipeline name to ng-app-pipeline and select New Service Role for setup role service as it is our new brand pipeline. After setting the pipeline name, click next for the next step.
 In step 2 of pipeline creation, we have to provide our source control from where it will get our code to build and deploy to s3. In our case, we will select Github as we pushed our code to Github. After selecting Github, click on the
In step 2 of pipeline creation, we have to provide our source control from where it will get our code to build and deploy to s3. In our case, we will select Github as we pushed our code to Github. After selecting Github, click on the Connect to Github button and provide your repository with its production branch, which is usually master for most of us, and click next for the next step.
 Now, in the Add Build Stage step, we have to provide the service we are using to create a staging build, so we select the
Now, in the Add Build Stage step, we have to provide the service we are using to create a staging build, so we select the AWS CodeBuild service, which is a service for AWS. You can also select Jenkins, if you are using it. Select your region and create a new project for it. A new window will open and you will provide details of your build project.
In project configuration
Provide a project name for your build project, it can be any name you want.
In Environment,
Select the:
- operating system: ubuntu
- Runtime: Standard
- Image:aws/codebuild/standard:1.0
- Image Version: always use the latest image for this runtime version
Now, click on Continue to CodePipeline to create the build project. After successfully creating a building project, click next for the deploy stage.
 Now, Select s3 as the deploy provider as we will host our app on AWS s3. You can choose which region you are using, but for the bucket option, we have to create a new bucket or select an existing bucket. This bucket will host our application build files, but make sure to check
Now, Select s3 as the deploy provider as we will host our app on AWS s3. You can choose which region you are using, but for the bucket option, we have to create a new bucket or select an existing bucket. This bucket will host our application build files, but make sure to check Extract file before deploy because after build process our build files have archived and we have to extract build archive to files for storing in s3. After these steps, click next to review all of the configuration steps you made before.
After reviewing, click on the create pipeline button and you'll see your pipeline for source; then, build and deploy. 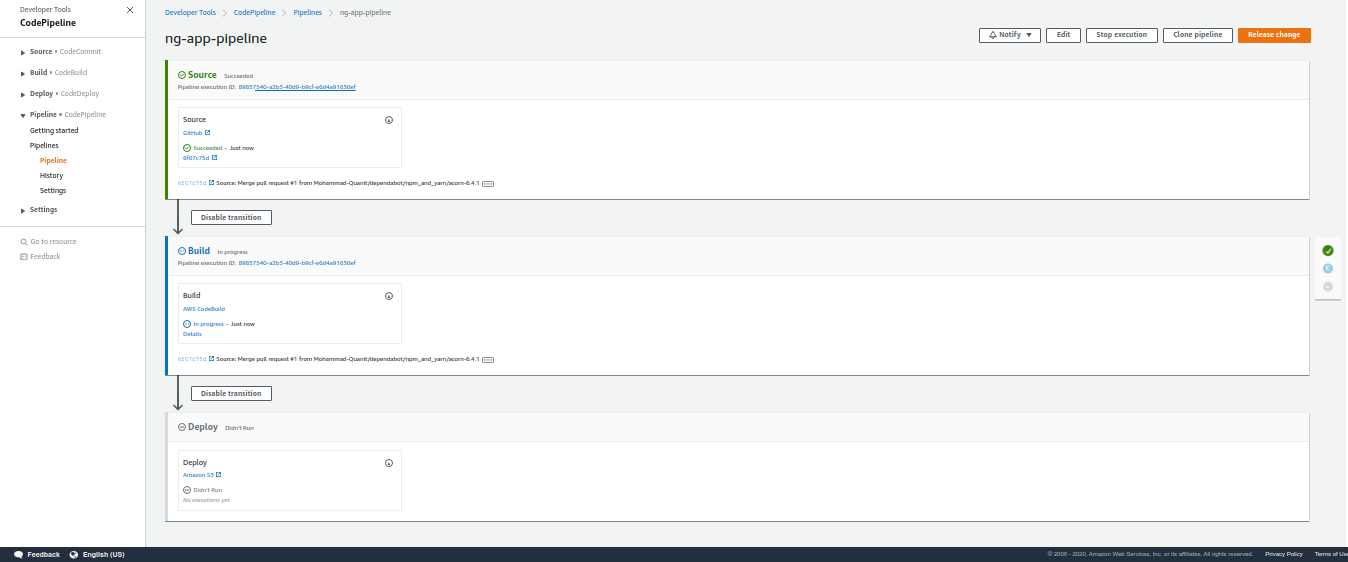
Buildspec.yaml
We have just set up the automation process in AWS CodePipeline service, now we have to create buildspec.yaml file in the root folder of our angular project. This is an important part of Continuous Integration, so we have to add our scripts carefully, otherwise, the build process will not succeed.
Here's what a buildspec.yaml file looks like:
version: 0.1 phases: install: commands: - echo installing nodejs... - curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_12.x | bash - - apt-get install -y nodejs - echo installing yarn... - curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | apt-key add - - echo "deb https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/ stable main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/yarn.list - apt install --no-install-recommends yarn pre_build: commands: - echo installing dependencies... - npm i -g @angular/cli - npm install build: commands: # - echo testing... # - echo building... - ng build --prod artifacts: files: - "**/*" discard-paths: no base-directory: dist/your-app-name Buildspec.yaml consists of phases of scripts. For example, the phases part of the first script is for installing nodejs with yarn. Let's look it one by one:
1) curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_12.x | bash -
This command is responsible for downloading node.js version 12 tar file in the ubuntu container (environment for hosting our app).
2) apt-get install -y nodejs
If you're familiar with ubuntu, you'll know what apt-get does. It will install node.js in our container from the downloaded tar file.
3) curl -sS https://dl.yarnpkg.com/debian/pubkey.gpg | apt-key add -
This command is for downloading the yarn package manager tar file. It's not mandatory to do it, but I prefer it over npm commands.
4) apt install --no-install-recommends yarn
This command is for installing the yarn package manager.
Now, in Pre-Build section, we have to provide commands for installing dependencies of the project,
4) npm i -g @angular/cli
This command will be responsible for installing angular cli globally so that we can create builds by typing ng build. It's a mandatory step; if this step is not done, it will not create a build.
5) npm install
This command will install all project-related dependencies required to run our app.
Now, in the build section, we have to provide commands to create a build of our project.
6) ng build --prod
It will create a production build of the angular project.
Now, in artifacts section, we have to provide files and base-directory names from where it will get build files after creating production build.
7) files "**/*"
By this command, it will get all build files and upload them into the AWS S3 services, which is where they will be hosted.
8) base-directory: dist/your-app-name
This will be the directory where your build files are.
Now, after creating buildspec.yaml file in root, push your code to your repository's master branch and it will automatically get your source code, create a build, and deploy it to S3.

You can see from the above image that it will start building our project – you can see the logs from the details button.
Alright, when everything goes perfect, go to S3 service from AWS console and search your bucket. By going to your bucket you'll see your build files. Now, go to the Properties tab and click static website hosting card. Check on Use this bucket to host a website option and write index.html in the index and error document fields and save it. You'll see an endpoint of your application, open a new chrome tab, and boom, your site is live on AWS S3.
Do try some changes in your code, push again to master, after creating build, and deploy. It will show you the latest changes in your live app.
So that's it for automating your angular app to deployment. By the way, this process is the same for react, vue, or any framework - you just have to manipulate buildspec.yaml file scripts according to your scenario.
I hope you have learned something out of it. Please follow me here for more content like this.
Peace ✌️ ✌️
CONTRIBUTOR
Mohammad Quanit
Source: https://www.educative.io/answers/automate-angular-application-deployment-via-aws-codepipeline
0 Response to "Continuous Delivery Using Buildspecyml Aws Agular"
Postar um comentário